Articles contributed by the community, curated for your enjoyment and reading.
Filters
Reset8 Best Practices for Implementing SAST
Code vulnerabilities often go unnoticed, leaving software exposed to threats. Yet many developers overlook a potent tool in their security suite: Static Application Security Testing (SAST). But here’s the thing – implementing SAST the right way takes more than just running a scan. You need a solid plan and approach. In this article, we’ll explore the best practices for implementing SAST into your workflow to keep your code base secure. What is SAST? SAST stands for Static Application Security Testing. It’s a way to check your code for security issues before you even run it. SAST tools dig into your code’s structure and detect issues like buffer overflows, SQL injection risks, and other vulnerabilities. The goal is to catch these problems early, preventing potential security threats from becoming real-world incidents. Head on to our blog on What is SAST to learn more. Now, where does this fit in the SDLC? Well, it’s not just a one-and-done deal. SAST is most effective when it’s woven throughout the development process. You start early, ideally when you’re still writing code. This way, you catch vulnerabilities before they turn into bigger issues. But it doesn’t stop there. You keep running SAST checks at different stages – during code reviews, before merging into the main branch, and definitely before pushing to production. The ultimate goal is to catch and fix security bugs early, saving time, money, and issues down the road. Understood. Here’s a revised version with formal subheadings and a more human-like explanation style: Benefits of Static Application Security Testing (SAST) Early Vulnerability Detection SAST finds security issues in the code before the application is even run. This means we can fix problems much earlier in the development process. It’s a lot easier and cheaper to fix issues when we’re still writing the code, rather than after we’ve built the whole application. Efficient Handling of Large Codebases As our projects get bigger, it becomes really hard for developers to manually check every line of code for security issues. SAST tools can handle massive amounts of code quickly and consistently. They don’t get tired or miss things because they’re in a hurry. Regulatory Compliance Support Many industries have tight regulations around software security, and SAST makes it easier to stay compliant. It provides detailed logs of all our security scans, so when audits come up, we’ve got solid proof that we’re taking security seriously and doing things right. Reduced Remediation Costs Fixing security problems after the software is released is expensive. It can cost much more than fixing the same issue during development. By catching problems early, SAST saves a lot of money in the long run. Multi-Language Support Most SAST tools work with many different programming languages. This is great for teams that use multiple languages in their projects. We can apply consistent security checks across all our code, regardless of the language in which it’s written. Integration with Development Workflows Modern SAST tools are designed to fit into existing development processes. They can be set up to run automatically whenever code is changed. This means security checks happen continuously without slowing down development. Security Posture Tracking SAST gives us data about our security status over time. We can see if we’re improving, where we commonly make mistakes, and what areas need more focus. This helps us get better at secure coding practices across the whole team. 8 Best Practices for Implementing SAST Start Security Checks Early Start using SAST tools as soon as you begin coding. Don’t wait until the end. Run scans during requirements gathering, design, coding, and testing phases. This helps catch issues early when they’re easier and cheaper to fix. For example, if you’re working on a new feature, run a scan on that specific code before merging it into the main branch. This prevents vulnerabilities from piling up. Establish Risk-Based Prioritization Protocols When SAST tools generate findings, don’t treat all issues equally. Set up a system to rank vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. Consider your organization’s specific risks and priorities. For instance, if you’re handling sensitive customer data, prioritize fixes for any potential data leakage issues. This approach ensures you’re tackling the most critical problems first. Customize SAST Rules and Configurations Out-of-the-box SAST tools often flag many false positives. Take time to tune your tool’s settings. Adjust rules based on your codebase, frameworks, and libraries. This might involve excluding certain files or directories or modifying sensitivity levels for specific checks. It’s a bit of work upfront, but it pays off by reducing noise and helping your team focus on real issues. Integrate Automated SAST Scans in CI/CD Pipeline Set up your SAST tools to run automatically with each code commit or pull request. This makes security checks a routine part of development. For example, configure your CI/CD pipeline to trigger a SAST scan whenever code is pushed to the repository. If issues are found, have the system notify developers or even block the merge until critical problems are resolved. Develop KPIs Focused on Vulnerability Remediation Instead of just counting the number of open bugs, track how many issues are actually being fixed. This gives a better picture of your security improvement. Set up dashboards that show trends in vulnerability remediation over time. Are high-severity issues being addressed quickly? Is the overall number of vulnerabilities decreasing? These metrics help demonstrate the value of your SAST efforts to management. Implement Regular SAST Tool Evaluations The field of application security is always evolving. New types of vulnerabilities emerge, and SAST tools improve to detect them. Schedule regular assessments of your SAST tools. Are they still meeting your needs? Are there new features or alternatives that could enhance your security posture? This might involve running pilot tests with different tools or attending security conferences to stay informed about the latest developments. Conduct Regular SAST Tool Training for Developers Your SAST tool is only as good as the people using it. Make sure your dev team knows how to use it properly. Run regular training sessions. Show them how to interpret results, how to avoid common pitfalls, and how to write code that’ll sail through scans. The more they understand the tool, the more effective your whole security process becomes. Establish a Feedback Loop for Continuous Improvement SAST isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it deal. Use the data from your scans to keep getting better. Look for patterns in the issues that come up. Maybe there’s a certain type of vulnerability that keeps popping up – that’s a sign you need more training in that area. Or maybe certain parts of your code are always clean – what are those developers doing right? Learn from your successes and failures to keep improving your security game. Why Choose CloudDefense.AI for SAST? Comprehensive Scanning CloudDefense.AI’s SAST solution isn’t a basic scan-and-go tool—it’s engineered to analyze your application’s entire codebase with precision. Security isn’t just about finding vulnerabilities; it’s about finding them at the right time. Our SAST tool integrates seamlessly into every stage of the software development lifecycle, from the earliest design phases to pre-deployment readiness. This approach ensures that security issues are identified and resolved before they can become costly problems in production. Automated Code Remediation We understand that manual fixes are inefficient and prone to delays, especially in fast-moving development cycles. That’s why our SAST solution focuses heavily on automation. When a vulnerability is detected, the system provides a detailed breakdown of the issue and delivers clear remediation steps. No vague reports or guesswork—just actionable insights that developers can immediately use to address the problem. This reduces downtime and accelerates the development pipeline without compromising security. Broad Language Support Modern development teams work across a variety of languages and platforms, so flexibility is critical. Our SAST tool supports an extensive range of languages, including C, C++, Docker, .NET, Go, Java, JavaGradle, JavaMaven, Kotlin, Kubernetes, JavaScript, Objective-C, PHP, Python, Ruby, Rust, Secrets, Terraform. We also cover essential frameworks like Kubernetes, Terraform, and JavaMaven. No matter your stack, we’ve got you covered. Compliance with Industry Security Standards Compliance is a non-negotiable part of modern software development, and we make it easy for you to meet the highest security benchmarks. Our SAST solution is built to ensure alignment with OWASP Top 10, and CWE Top 25 (2019–2021). By integrating these standards into your development workflow, you don’t just check a compliance box—you elevate the overall security posture of your application. Actionable Insights Detailed reporting is a core feature of our SAST tool. When vulnerabilities are flagged, you’re not left wondering what to do next. We provide clear, structured insights that explain the issue, its potential impact, and the steps required to fix it. Beyond fixing immediate problems, our reporting includes metrics to help you measure your progress and continuously improve code quality over time. We use a variety of security tools to check every part of your application. We don’t just look at one layer—we examine the whole thing, giving you a more complete picture of its security. If you’re interested in seeing how Clouddefense.AI can improve your application security, we invite you to schedule a demo. Our team would be happy to show you our SAST tool in action and discuss how we can address your specific security needs. Original Article - https://www.clouddefense.ai/best-practices-for-implementing-sast/
15 Best Practices for High-Performance .NET Applications
In the competitive landscape of software development, performance is a crucial factor that can make or break the success of your .NET applications. Whether you’re building enterprise-level web applications, APIs, or microservices, optimizing performance is essential for delivering a seamless user experience and maintaining competitiveness in the market. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore 15 best practices that can help you maximize the performance of your .NET applications, complete with detailed explanations and code examples. 1. Utilize Caching Caching is a fundamental technique for improving the performance of .NET applications by storing frequently accessed data in memory. This reduces the need to retrieve data from slower data sources such as databases. In .NET, you can leverage the MemoryCache class from the Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory namespace. public class ProductController : ControllerBase { private readonly IMemoryCache _cache; private readonly IProductRepository _productRepository; public ProductController(IMemoryCache cache, IProductRepository productRepository) { _cache = cache; _productRepository = productRepository; } [HttpGet("{id}")] public IActionResult GetProduct(int id) { var cacheKey = $"Product_{id}"; if (!_cache.TryGetValue(cacheKey, out Product product)) { product = _productRepository.GetProduct(id); if (product != null) { // Cache for 10 minutes _cache.Set(cacheKey, product, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10)); } } return Ok(product); } } In this example, the MemoryCache is used to store product data retrieved from the database. If the product is not found in the cache, it’s fetched from the database and then stored in the cache with an expiration time of 10 minutes. 2. Optimize Hot Code Paths Identify and optimize hot code paths, which are sections of code that are frequently executed and contribute significantly to the overall runtime of your application. By optimizing these paths, you can achieve noticeable performance improvements. public class OrderProcessor { public void ProcessOrder(Order order) { foreach (var item in order.Items) { // Optimize this section for performance } } } In this example, the ProcessOrder method represents a hot code path responsible for processing order details. It should be optimized for performance, possibly by using more efficient algorithms or data structures within the loop. 3. Use Asynchronous APIs Leverage asynchronous programming to handle multiple operations concurrently, improving scalability and responsiveness. Asynchronous APIs in .NET can be utilized using the async and await keywords. public async Task<IActionResult> GetDataAsync() { var data = await _dataService.GetDataAsync(); return Ok(data); } In this example, the GetDataAsync method asynchronously retrieves data from a service. This allows the application to continue executing other tasks while waiting for the data to be fetched. 4. Asynchronize Hot Code Paths Convert hot code paths to asynchronous operations to further enhance concurrency and responsiveness, especially in performance-critical sections of your code. public async Task ProcessOrdersAsync(List<Order> orders) { foreach (var order in orders) { // Asynchronously process each order await ProcessOrderAsync(order); } } private async Task ProcessOrderAsync(Order order) { // Asynchronously process order details await Task.Delay(100); // Example asynchronous operation } In performance-critical code paths, consider making asynchronous versions of methods to allow for non-blocking execution and improved concurrency. 5. Implement Pagination for Large Collections When dealing with large datasets, implement pagination to fetch data in smaller chunks, reducing memory consumption and improving performance. public IActionResult GetProducts(int page = 1, int pageSize = 10) { var products = _productRepository.GetProducts() .Skip((page - 1) * pageSize) .Take(pageSize) .ToList(); return Ok(products); } In this example, the GetProducts method retrieves a paginated list of products from the repository, allowing the client to request data in smaller chunks. 6. Prefer IAsyncEnumerable Use IAsyncEnumerable<T> for asynchronous enumeration of collections to prevent synchronous blocking and improve efficiency, especially with large datasets. public async IAsyncEnumerable<int> GetNumbersAsync() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { await Task.Delay(100); // Simulate asynchronous operation yield return i; } } 7. Cache Large Objects and Use ArrayPool Optimize memory usage by caching frequently used large objects and managing large arrays with ArrayPool<T>. public void ProcessLargeArray() { var largeArray = ArrayPool<int>.Shared.Rent(100000); // Process large array ArrayPool<int>.Shared.Return(largeArray); } 8. Optimize Data Access and I/O Minimize roundtrips and latency by optimizing data access and I/O operations, such as database queries and external API calls. public async Task<IActionResult> GetCachedDataAsync() { var cachedData = await _cache.GetOrCreateAsync("cached_data_key", async entry => { // Retrieve data from database or external service var data = await _dataService.GetDataAsync(); // Cache for 15 minutes entry.AbsoluteExpirationRelativeToNow = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(15); return data; }); return Ok(cachedData); } 9. Use HttpClientFactory Manage and pool HTTP connections efficiently with HttpClientFactory to improve performance when making HTTP requests. public async Task<IActionResult> GetRemoteDataAsync() { var client = _httpClientFactory.CreateClient(); var response = await client.GetAsync("https://api.example.com/data"); if (response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { var data = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); return Ok(data); } else { return StatusCode((int)response.StatusCode); } } 10. Profile and Optimize Middleware Components Profile and optimize frequently-called middleware components to minimize their impact on request processing time and overall application performance. // Example middleware component public class LoggingMiddleware { private readonly RequestDelegate _next; private readonly ILogger<LoggingMiddleware> _logger; public LoggingMiddleware(RequestDelegate next, ILogger<LoggingMiddleware> logger) { _next = next; _logger = logger; } public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { // Log request information _logger.LogInformation($"Request: {context.Request.Path}"); await _next(context); } } 11. Use Background Services for Long-Running Tasks Offload long-running tasks to background services to maintain application responsiveness and prevent blocking of the main application thread. public class EmailSenderService : BackgroundService { protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken) { while (!stoppingToken.IsCancellationRequested) { // Check for pending emails and send them await SendPendingEmailsAsync(); // Wait for some time before checking again await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5), stoppingToken); } } } 12. Compress Responses to Reduce Payload Sizes Enable response compression to reduce the size of HTTP responses, minimizing network bandwidth usage and improving overall application performance, especially for web applications. // Configure response compression in Startup.cs public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddResponseCompression(options => { options.EnableForHttps = true; options.MimeTypes = new[] { "text/plain", "text/html", "application/json" }; }); } 13. Stay Updated with Latest ASP.NET Core Releases Ensure your application is up-to-date with the latest ASP.NET Core releases to leverage performance improvements and new features provided by the framework. 14. Avoid Concurrent Access to HttpContext Avoid concurrent access to HttpContext as it is not thread-safe. Access to HttpContext should be synchronized to prevent race conditions and ensure application stability. // Example usage in controller action public IActionResult GetUserData() { var userId = HttpContext.User.FindFirst(ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier)?.Value; // Retrieve user data using userId return Ok(userData); } 15. Handle HttpRequest.ContentLength Appropriately Handle scenarios where HttpRequest.ContentLength is null to ensure robustness and reliability in request processing, especially when dealing with incoming HTTP requests. // Example usage in controller action public async Task<IActionResult> ProcessFormDataAsync() { if (Request.ContentLength == null) { return BadRequest("Content length is not provided"); } // Process form data return Ok(); } By implementing these 15 best practices in your .NET applications, you can significantly enhance their performance, scalability, and user experience, enabling you to meet the demands of modern, high-performance software development. Remember, performance optimization is an ongoing process, so continuously monitor and refine your application to ensure it remains optimized for maximum efficiency.
How to Effectively Block Spam in Contact Forms with .NET Core 8.0 MVC
How to Prevent Spam in Contact Forms with .NET Core 8.0 MVC – A Step-by-Step Guide Dealing with spam submissions in your lead or contact forms can be incredibly frustrating—especially when you’ve already implemented CAPTCHA and other spam prevention measures. But what if I told you there's a simple yet effective solution that could help you significantly reduce unwanted form submissions? In this post, I’ll walk you through a quick tip for blocking spam in your forms using .NET Core 8.0 MVC. While this solution is tailored to .NET Core, the logic can be adapted to other technologies as well, making it versatile and easy to implement across different platforms. Why Spam Forms Are a Problem Spammers often use automated bots or scripts to find and submit contact or lead forms on websites, flooding your inbox with irrelevant, sometimes harmful, content. CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) has been a popular solution for this, but it’s not foolproof. Bots are becoming smarter and can sometimes bypass CAPTCHA mechanisms. Luckily, there’s a much simpler method to keep spammers out while ensuring legitimate visitors can still submit forms without a hitch. The Simple Trick: Adding a Hidden Field The solution? A hidden input field. It’s a basic technique that prevents bots from submitting forms, as they typically “fill out” all fields, including hidden ones. By checking if this field is empty when the form is submitted, you can easily determine whether it was filled out by a bot or a human. Let’s take a look at how to implement this in a .NET Core 8.0 MVC application. Step 1: Build the Contact Form Here’s a basic contact or lead form that users can fill out. This example uses .NET Core MVC syntax: <form asp-action="contact" asp-controller="home" method="post"> <input class="form-control" type="text" maxlength="255" asp-for="FullName" placeholder="Your Name" required> <input class="form-control" type="email" maxlength="255" asp-for="Email" placeholder="Your Email" required> <input class="form-control" type="text" pattern="^[0-9]*$" maxlength="15" asp-for="Phone" placeholder="Your Phone with Country Code"> <textarea class="form-control" asp-for="Message" cols="40" rows="5" maxlength="1000" placeholder="Your Message" required></textarea> </form> Now, let’s add a hidden field to this form: <input class="additional-note" type="text" style="display:none;"> Step 2: Implement the Spam Check Logic When the form is submitted, we check whether the hidden field is filled out. If it’s empty, the submission is likely from a human. If it's not, it’s probably a bot, and we can discard the submission. In the controller, add the logic to handle this check: [HttpPost("contact")] [ValidateReCaptcha] public async Task<IActionResult> Contact(LeadModel model) { if (!ModelState.IsValid) return View(); try { bool result = await _contactService.SaveLead(model); TempData["success"] = result ? "We have received your request, and we'll get back to you shortly!" : "Sorry, we couldn't process your request."; return RedirectToAction("contact", "home"); } catch (Exception ex) { TempData["fail"] = "Sorry! Something went wrong while processing your request."; _logger.LogError(ex, $"Error occurred while saving lead - {Helper.Dump(model)}"); } return View(); } Step 3: Business Logic Service In the business logic service, we need to ensure that the lead is saved only if the hidden field is empty (indicating it wasn’t filled out by a bot): public async Task<bool> SaveLead(LeadModel? leadModel) { if (leadModel == null || !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(leadModel.RepeatLead)) return false; // Discard leads where the hidden field is filled out (likely spam). var lead = _mapper.Map<Lead>(leadModel); return await _contactRepository.SaveLead(lead); } How It Works: Bots vs Humans: Bots usually fill out all fields, including hidden ones, whereas humans won’t interact with hidden fields. Quick Spam Detection: If the hidden field is filled out, we treat the submission as spam and reject it. Seamless User Experience: Legitimate users can still submit the form as usual without any interruption. Why This Works Spammers use automated scripts to find and submit forms, but they don’t know about hidden fields that are intentionally left blank. This simple trick helps filter out spam without adding extra layers of complexity or affecting user experience. Plus, it’s incredibly easy to implement with .NET Core MVC. Conclusion: A Simple Yet Effective Spam Prevention Solution Implementing a hidden field in your forms is a quick and effective way to fight spam without over-complicating things. This approach works across various technologies, so feel free to adapt it to your tech stack. By using this method, you can keep your contact forms clean and only receive genuine submissions. 💪 What Do You Think? Have you tried similar techniques to block spam in your forms? What methods have worked best for you? Share your thoughts in the comments below! Also, feel free to share this post with anyone who might benefit from a spam-free experience on their website. Let’s keep our forms secure and user-friendly!
Understanding the Difference Between const and readonly in Csharp
🚀 C#/.NET Tip - Const vs Readonly 💡 💎 Understanding the Difference Between const and readonly in C# 🔹 Const: Constants are static by default. They must be assigned a value at compile-time. Can be declared within functions. Each assembly using them gets its own copy of the value. Can be used in attributes. 🔹 Readonly: Must be assigned a value by the time the constructor exits. Evaluated when the instance is created. Static readonly fields are evaluated when the class is first referenced. Example: public class MathConstants { public const double Pi = 3.14159; public readonly double GoldenRatio; public MathConstants() { GoldenRatio = (1 + Math.Sqrt(5)) / 2; } } Explanation: Pi is a const and its value is fixed at compile-time. It cannot be changed and is the same across all instances. 2. GoldenRatio is a readonly field, which is calculated at runtime when an instance of MathConstants is created. This allows for more flexibility as the value can be set in the constructor. This example highlights how const is used for values that are truly constant and known at compile-time, while readonly is used for values that are determined at runtime but should not change after being set. I hope this helps! 😊
Mastering In-Memory Caching in ASP.NET Core
In-memory caching stands as a cornerstone technique in optimizing the performance and scalability of ASP.NET Core applications. By storing frequently accessed data in memory, developers can drastically reduce the need to fetch information from slower data sources such as databases or external APIs. This leads to faster response times, improved resource utilization, and ultimately, a superior user experience. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of in-memory caching, exploring its benefits, setup process, implementation strategies, and best practices. Understanding the Significance of In-Memory Caching: Accelerated Performance The primary advantage of in-memory caching lies in its ability to boost application performance. Retrieving data from memory is inherently faster than fetching it from disk or over the network. Consequently, in-memory caching significantly reduces latency, ensuring that users receive timely responses to their requests. Reduced Load on Data Sources By caching frequently accessed data, ASP.NET Core applications can alleviate the burden on external data sources, such as databases or web services. This reduction in load translates to improved scalability, as the application can handle more concurrent users without compromising performance. Enhanced User Experience In-memory caching contributes to an enhanced user experience by providing quick access to frequently requested information. Whether it’s product listings, user profiles, or dynamic content, caching ensures that data is readily available, resulting in a smoother and more responsive application interface. When to Use In-Memory Caching: While in-memory caching offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to use it judiciously and considerately. Here are some scenarios and considerations for leveraging in-memory caching effectively in ASP.NET Core applications: Frequently Accessed Data In-memory caching is most beneficial for data that is accessed frequently but changes infrequently. Examples include reference data, configuration settings, and static content. Caching such data in memory reduces the overhead of repeated database or file system accesses, leading to significant performance improvements. High-Volume Read Operations Applications with high-volume read operations, such as e-commerce platforms with product listings or content management systems with articles, can benefit greatly from in-memory caching. By caching frequently accessed data, these applications can handle large numbers of concurrent users while maintaining responsiveness and scalability. Expensive Computations or Queries In-memory caching can also be valuable for caching the results of expensive computations or database queries. By caching the computed or queried results, subsequent requests for the same data can be served quickly from memory, avoiding the need to repeat the costly operation. User Session Data For applications that store user-specific data during a session, such as shopping cart contents or user preferences, in-memory caching can provide a fast and efficient mechanism for managing session state. By caching session data in memory, the application can minimize latency and improve user experience. Temporary Data Storage In-memory caching can serve as a temporary data storage solution for transient data that doesn’t need to be persisted long-term. Examples include temporary authentication tokens, short-lived cache keys, or data used for the duration of a user session. Caching such data in memory can help reduce database load and improve application performance. Setting Up In-Memory Caching in ASP.NET Core: Configuring Services Enabling in-memory caching in an ASP.NET Core application begins with configuring the necessary services. This can be achieved in the Startup.cs file within the ConfigureServices method. public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddMemoryCache(); // Add caching services // Additional service configurations... } By invoking the AddMemoryCache() method, developers incorporate the essential caching services into the application’s service container. Injecting IMemoryCache To utilize in-memory caching within various components of the application, developers need to inject the IMemoryCache interface. This is typically done through constructor injection in controllers, services, or other relevant classes. using Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory; public class ProductController : ControllerBase { private readonly IMemoryCache _cache; public ProductController(IMemoryCache cache) { _cache = cache; } // Controller actions... } Implementing In-Memory Caching Strategies: With in-memory caching configured and IMemoryCache injected into the application components, developers can proceed to implement caching logic tailored to their specific use cases. Let’s explore a detailed example of caching product data in an ASP.NET Core web API. Example: Caching Product Data Suppose we have an endpoint in our web API for retrieving product details by ID. We want to cache the product data to improve performance and reduce database load. [HttpGet("{id}")] public async Task<IActionResult> GetProduct(int id) { // Attempt to retrieve the product from the cache if (_cache.TryGetValue($"Product_{id}", out Product cachedProduct)) { return Ok(cachedProduct); // Return the cached product } // If not found in cache, fetch the product from the data source (e.g., database or external API) Product product = await _productService.GetProductById(id); if (product != null) { // Cache the product with an expiration time of 5 minutes _cache.Set($"Product_{id}", product, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5)); return Ok(product); // Return the fetched product } else { return NotFound(); // Product not found } } In this example: We attempt to retrieve the product with the given ID from the cache using TryGetValue(). If the product is found in the cache, it’s returned directly from memory. If not found, we fetch the product from the data source (e.g., database or external API) and cache it using Set() with an expiration time of 5 minutes. Syntax Examples: Here are examples of syntax for adding, removing, and other operations related to in-memory caching in ASP.NET Core using the IMemoryCache interface: Adding Data to Cache: _cache.Set("CacheKey", cachedData, TimeSpan.FromMinutes(10)); // Cache data with a key and expiration time Retrieving Data from Cache: if (_cache.TryGetValue("CacheKey", out CachedDataType cachedData)) { // Data found in cache, use cachedData } else { // Data not found in cache, fetch from source and cache it } Removing Data from Cache: _cache.Remove("CacheKey"); // Remove data from cache by key Clearing All Cached Data: _cache.Clear(); // Clear all data from cache Checking if Data Exists in Cache: if (_cache.TryGetValue("CacheKey", out CachedDataType cachedData)) { // Data exists in cache } else { // Data does not exist in cache } These syntax examples demonstrate how to perform common operations related to in-memory caching in ASP.NET Core using the IMemoryCache interface. From adding and retrieving data to removing entries and configuring cache options, developers can effectively utilize in-memory caching to optimize performance and enhance the user experience of their applications. Conclusion: In-memory caching represents a cornerstone technique for optimizing the performance and scalability of ASP.NET Core applications. By strategically caching frequently accessed data in memory, developers can minimize latency, reduce load on data sources, and deliver a superior user experience. Armed with a solid understanding of in-memory caching concepts and implementation strategies, developers can leverage this powerful tool to build high-performing and responsive applications that meet the demands of modern users. Original Article - Mastering In-Memory Caching in ASP.NET Core
Join Our Talent Pool: Explore Various Job Opportunities!
The open positions as of today 07 Feb 2025 are (How to apply is mentioned below): Client: Infosys Position Name: Oracle OAF Experience: 5 years Location: Remote Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Oracle E-Business Suite ERP Developer Experience: 5 years Skills Required: Minimum 5 years of role experience as Oracle EBS Techno Functional consultant. Experience in designing and developing financial solutions on Oracle eBusiness Suite R12 platform, with focus on Procure to Pay (P2P), Record to Report (R2R), and AR modules and global rollouts. Extensive hands-on development and functional experience and proficiency in SQL and PL/SQL, Oracle Workflow, BI publisher, AME, Oracle Forms, Oracle Reports, UNIX Shell scripts, Java, and OA Framework. Experience in system integration and familiarity with enterprise application integration (EAI) technologies. Experience and knowledge of Oracle modules, Apache/IIS, WebLogic application server, and other middleware platforms would be a plus. Experience in SAP Concur and Ariba application would be a plus. Extensive development knowledge of Oracle eBusiness Suite R12 (Account Receivable, Purchasing, Payables, Payments, EBTax, Cash Management, Fixed Assets, General Ledger, Sub ledger Accounting, XML Gateway, System Administration, TCA Architecture) and related systems. Experience in and understanding of the software development lifecycle and methodologies and Finance operations (accounts payable, sourcing, accounting, financial internal controls) business process knowledge in a global setting. Location: Bangalore Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Big Data Engineer with Airflow, Python Experience: 5+ years Location: Bengaluru Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Oracle E-Business Suite (ERP) Test Engineer Experience: 5+ years Skills Required: ERP Software Test Engineer will play a key role to partner with the application Support and Development teams for SAP Ariba, SAP Concur, and Oracle ERP (Oracle eBusiness Suite R12- Purchasing, Accounts Payables, General Ledger, EBTax, Fixed Assets, and Accounts Receivables) and other Finance applications. ERP Software Test Engineer will be performed against global initiatives, enhancements, and day-to-day operational Production defects. Tasks include creation of Test Plans, Test Case Creation, Test Data Creation, Manual Testing, Issue Management Resolution, and Documentation. Ability to comprehend complex Business requirements and technical solutions, mapping into Test Cases, and Test Scripts. Manage defects from identification to completion. Assist to standardize reporting and metrics on deliverables by the QA team, including defect logging and status reporting. ERP Software Test Engineer is expected to create SQL queries against database to troubleshoot, create ad-hoc reporting as needed. Work with limited direction, usually within a complex environment, to drive delivery of solutions and meet service levels. Able to work on multiple projects and initiatives with different/competing timelines and demands. Location: Remote Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Database & Middleware Engineer/Administrator Experience: 4+ years Skills Required: Provide administration support for various databases, including MS SQL Server, MySQL, and Postgres, ensuring smooth operation and quick issue resolution. Assist in the support and maintenance of Applications/Middleware and Platforms, including troubleshooting, patching, backups & recovery, and system updates. Regularly perform system maintenance tasks, including provisioning, installing, patching, securing, and auditing databases, middleware, and platforms to ensure optimal performance and compliance. Location: Remote Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Identity and Access Management (IAM) Consultant Experience: 5+ years Skills Required: This role will require technical knowledge on automation of application IAM data / Access Control List (ACL) into our IAM Governance tool (setting up automated IAM datafeeds through direct database connectivity, proxy sFTP service, other third-party data aggregator tools, etc.). This role requires a deep understanding of the IAM related risks and the relevant mitigating/compensating IAM controls and policies, including control attestation, control testing, and control artifact validations. This position is specialized in providing the end-to-end IAM life cycle including but not limited to the technical application enrollment into the centralized IAM Governance infrastructure, IAM services (weekly access data load into SailPoint, Access provisioning, access deprovisioning, rogue access remediation, orphaned access remediation, Separation of Duties (SOD) remediation, transfer/mover user access reviews, user access revalidation, non-user account credential rotation governance, etc.). Act as the IAM point of contact for a set of assigned applications and manage the enterprise end-to-end IAM lifecycle for these applications. This role will also require analytic skillsets on big data analytics, dashboarding, database query, etc. Location: Remote Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Data Platform Engineer Experience: 6+ years Skills Required: Cloud data platform engineer who designs, builds, and manages data storage and workflows in cloud environments. They ensure that data is secure, accessible, and processed efficiently. Data Platform Management and Optimization - designs, builds, and manages data storage and workflows/compute in cloud environments. Location: Remote Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Java Developer with Spring Boot & Microservices Experience: Total: 8+ years; Relevant: 5+ years Skills Required: Experience in the development of production-grade applications and services in Java. Hands-on development experience in Java 8, Spring Boot, Microservices. Good knowledge of Java 8 features - Collections, Generics, Authentication, Rest API, multi-threading. Location: Bangalore Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Oracle XStore Experience: 10 years with 7 years relevant Skills Required: Oracle DB, SQL, Core Java, Oracle Xstore Suite, XML Location: Pune, Chennai Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Java Developer with SpringBoot & Microservices Experience: 6+ years (Relevant Experience) Location: Chennai Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Java Developer with SpringBoot, Microservices, Kafka, SQL Experience: 6+ years (Relevant Experience) Location: Chennai, Bangalore, Hyderabad Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Scala Developer (pure Scala profile) Skills Required: Programming Language: They primarily use Scala, a language that combines functional and object-oriented programming paradigms. Responsibilities: Design application architecture, write clean Scala code, debug issues, test applications, optimize performance, collaborate with other developers, and ensure application scalability. Typical Applications: Big data processing, distributed systems, web applications, financial systems requiring high-performance transaction processing. Location: Pune, Kolkata, Hyderabad Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Python Lead Experience: 8+ years (relevant 7+ years) Location: Pune, Bangalore Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Client: Cybage Position Name: Python + DevOps (SRE) Experience: 4-9 years Skills Required: Working experience & knowledge in Python along with SRE; familiarity with Jenkins/CloudBuild, Ansible, and Cloud Computing platforms. Familiar working with containerization technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes. Location: Pune-Hybrid Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Client: QIncline Position Name: Sr. Automation Test Engineer (Java with Selenium) Experience: 8-9 years Location: Bangalore Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms Position Name: Oracle BRM Experience: 5-6 years Skills Required: Legacy to Target Mapping to BRM (OCS) - Prepaid System BRM Loading Mechanisms and previous experience worked on pin_bulk_loader (CMT Tool). Real-Time Data Loading. Fallout Scenarios: Scenario how to fix in case of Data failure, System Performance Issue, Synchronization Issues, TPS limit or any metrics to be followed based on previous migration experience, Data export method to follow for Reconciliation, Retry Mechanisms, Error Correction Frameworks, Performance Tuning, Backup and Recovery (Restore) DB. Location: Bangalore/Remote Rate: Contact for rate and payment terms I hope this format works better for you! Let me know if you need any further adjustments. How to apply I have strong relationships with many staffing companies and will be posting multiple job openings daily. Please sign up to receive daily alerts for new job postings. While we are currently developing an online application process, you can follow the steps below to apply in the meantime: Visit my LinkedIn profile: Mayur Lohite LinkedIn Send me a Invite or direct message (DM) with the name of the position you are interested in. Or post your linkedin link in comment so I will send you invite. I will connect you with the respective staffing agency. If LinkedIn didn't worked then just visit our contact page and write position name in first line and send us a message -> Contact Us Thank you for your interest, and I look forward to helping you find your next career opportunity!
Exploring the Zip Method in LINQ: A Game-Changer for Merging Sequences
Ever heard of the Zip method in LINQ? It's a powerful tool for merging sequences, and it's something every developer should have in their toolkit. Let's dive into how this method can simplify your coding life, especially with the enhancements introduced in .NET 6. What is the Zip Method? The Zip method in LINQ allows you to merge two or more sequences into one. Starting from .NET 6, you can combine up to three collections at once. The resulting sequence will match the length of the shortest collection, ensuring a neat and tidy merge. Why Use the Zip Method? Simplifies Code: The Zip method reduces the need for multiple foreach loops, making your code cleaner and more readable. Customizable Pairing: You can use a result selector to customize how the elements are paired together, giving you flexibility in how you merge your data. Efficiency: By merging sequences in a single step, you can improve the efficiency of your code. A Practical Example Let's look at a simple example using .NET Core: static void Main() { var numbers = new[] { 1, 2, 3 }; var words = new[] { "one", "two", "three" }; var zipped = numbers.Zip(words, (n, w) => $"{n} - {w}"); foreach (var item in zipped) { Console.WriteLine(item); } } In this example, we have two arrays: numbers and words. The Zip method combines these arrays into a single sequence where each element is a combination of an element from numbers and an element from words. The result is a sequence of strings like "1 - one", "2 - two", and "3 - three". Real-world Scenario Imagine you're working on a project that involves merging data from different sources, like combining sales figures with product names. The Zip method can be your go-to solution. It's like making a perfect masala chai, where each ingredient blends seamlessly to create something wonderful. Conclusion The Zip method in LINQ is a versatile and powerful tool that can make your coding tasks easier and more efficient. Whether you're working on a small project or a large-scale application, this method can help you merge sequences with ease. Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments below. If you found this post useful, follow me for more tech insights and don't hesitate to share this with your network! 🚀
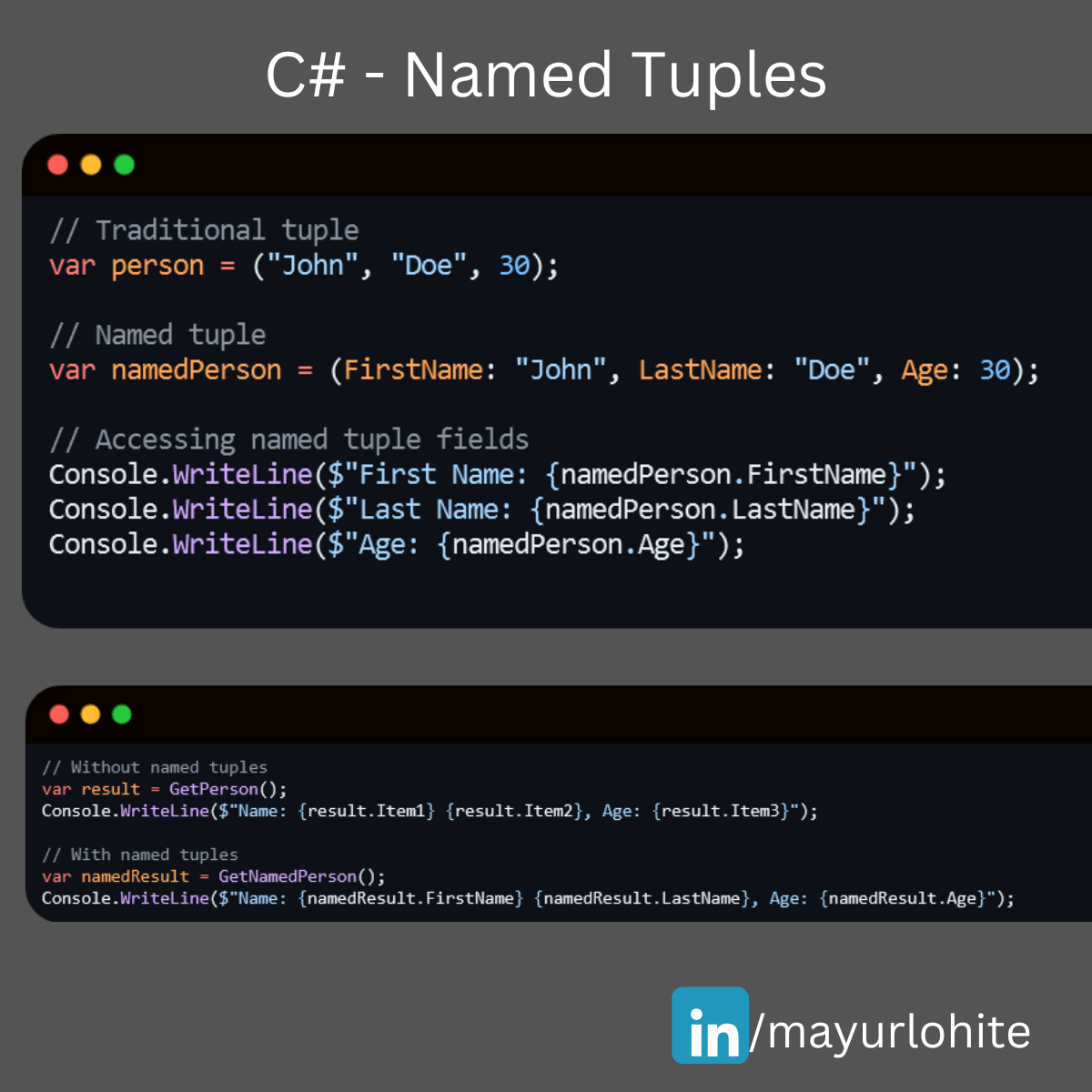
A Short tip to boost Your C# Skills with Named Tuples
Hey Mudmatter community! 👋 Are you looking to make your C# code more readable and maintainable? Named tuples might be just what you need! They allow you to create lightweight, self-descriptive data structures without the overhead of defining a full class. What are Named Tuples? Named tuples in C# provide a way to create a tuple with named fields, making your code more intuitive and easier to understand. Why Use Named Tuples? Readability: Named fields make it clear what each value represents. Convenience: No need to define a separate class or struct for simple data grouping. Immutability: Tuples are immutable by default, ensuring data integrity. Example - Traditional // Traditional tuple var person = ("John", "Doe", 30); // Named tuple var namedPerson = (FirstName: "John", LastName: "Doe", Age: 30); // Accessing named tuple fields Console.WriteLine($"First Name: {namedPerson.FirstName}"); Console.WriteLine($"Last Name: {namedPerson.LastName}"); Console.WriteLine($"Age: {namedPerson.Age}"); Benefits in Action, Improved Code Clarity: // Without named tuples var result = GetPerson(); Console.WriteLine($"Name: {result.Item1} {result.Item2}, Age: {result.Item3}"); // With named tuples var namedResult = GetNamedPerson(); Console.WriteLine($"Name: {namedResult.FirstName} {namedResult.LastName}, Age: {namedResult.Age}"); //Simplified Data Handling: // Method returning a named tuple (string FirstName, string LastName, int Age) GetNamedPerson() { return ("John", "Doe", 30); } Named tuples are a fantastic feature to enhance your C# projects. Give them a try and see how they can simplify your code! Happy coding! 💻✨
Boost your EF Core performance with bulk updates using ExecuteUpdate
🚀 Exciting News for EF Core Users! 🚀 The latest version of Entity Framework Core (EF Core 7) introduces a powerful new feature: Bulk Update! This feature significantly enhances performance when updating multiple records in your database. Let's dive into how it works and see a sample in action. What is Bulk Update? Bulk Update allows you to perform update operations on multiple entities directly in the database without loading them into memory. This is achieved using the new ExecuteUpdate method, which can be a game-changer for applications dealing with large datasets. Why Use Bulk Update? Performance: Reduces the number of database round-trips. Efficiency: Updates multiple records in a single SQL statement. Simplicity: Cleaner and more readable code. Sample Code Here's a quick example to illustrate how you can use the Bulk Update feature: context.Products .Where(p => p.Price > 100) .ExecuteUpdate(p => p.SetProperty(p => p.Discount, 10) .SetProperty(p => p.LastUpdated, DateTime.Now)); Improved Performance: Executes a single SQL update statement. Reduced Memory Usage: No need to load entities into memory. Cleaner Code: More concise and easier to maintain. Conclusion The Bulk Update feature in EF Core 7 is a fantastic addition for developers looking to optimize their data operations. Give it a try and see the performance improvements in your applications!
Supercharge Your EF Core Performance with BulkInsertAsync
🚀 Supercharge Your EF Core Performance with BulkInsertAsync! 🚀 Struggling with large data insertions in your .NET applications? EF Core’s BulkInsertAsync can be a game-changer. Just install EFCore.BulkExtensions from nuget. Here’s a quick guide to help you get started: Why Use BulkInsertAsync? 1. Efficiency: Inserts multiple records in a single database round trip. 2. Performance: Significantly reduces the time taken for bulk operations. 3. Simplicity: Easy to implement with minimal code changes. Example Let’s say we have a Student entity and we want to insert a large list of students into the database. using EFCore.BulkExtensions; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading.Tasks; public class Student { public int StudentId { get; set; } public string FirstName { get; set; } public string LastName { get; set; } public string Branch { get; set; } } public class ApplicationDbContext : DbContext { public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } } public async Task BulkInsertStudentsAsync(List<Student> students) { using var context = new ApplicationDbContext(); await context.BulkInsertAsync(students); } EF Core SaveChangesAsync: 1,000 records: 18 ms 10,000 records: 203 ms 100,000 records: 2,129 ms EF Core BulkInsertAsync: 1,000 records: 8 ms 10,000 records: 76 ms 100,000 records: 742 ms1 With BulkInsertAsync, you can handle large data operations efficiently and keep your application running smoothly. Give it a try and see the difference!